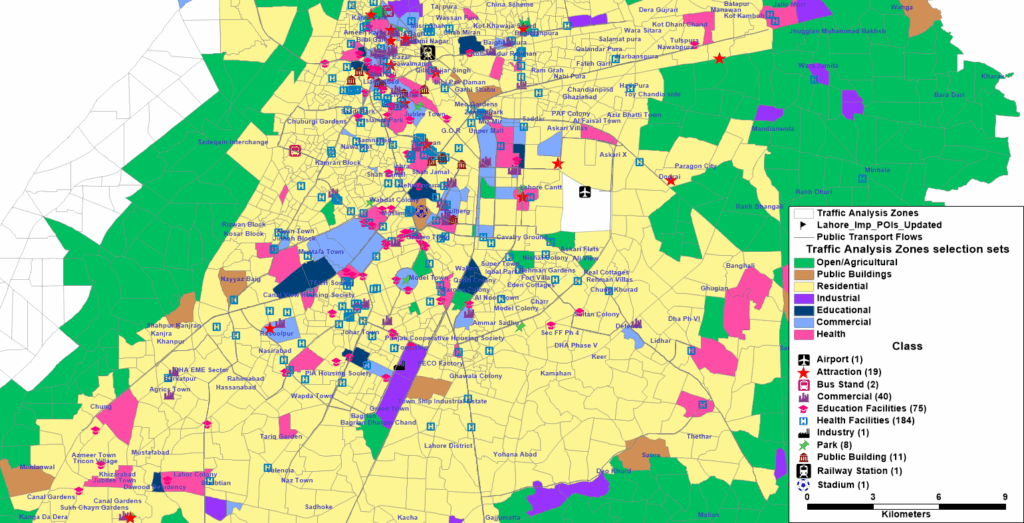
Ai Traffic Counting Software by Arterials
Simple, Accurate, Automatic
Learn More

Data-Driven Transportation Planning for Smarter Cities
Traffic impact studies | GIS services | Master Planning | Transportation Modelling

Arterials is a transportation consultancy specializing in integrated planning, traffic engineering, GIS analysis, and mobility modeling. We support better movement, safer infrastructure, and long-term urban growth.
- What is PCU (Passenger Car Unit) in Traffic Engineering?When analyzing roads, intersections, and traffic flow, engineers face a common challenge: vehicles are not all the same. A car, a motorcycle, a truck, and a rickshaw each take up different amounts of road space, move at… Read more: What is PCU (Passenger Car Unit) in Traffic Engineering?
- What is Rush Hour Traffic? How Engineers Calculate Peak Hour Traffic VolumesWhen most people talk about rush hour traffic, they’re thinking about the frustrating congestion on roads during the morning and evening commute. Transportation engineers use a more technical term for the same idea: peak hour traffic. Understanding… Read more: What is Rush Hour Traffic? How Engineers Calculate Peak Hour Traffic Volumes
- Traffic Impact Assessment (TIA) Guidelines for MunicipalitiesTraffic Impact Assessments (TIAs) are critical tools that help municipalities understand how new developments will affect local transportation networks. These TIA guidelines provide a practical framework for preparing and reviewing TIAs in municipalities that do not yet… Read more: Traffic Impact Assessment (TIA) Guidelines for Municipalities
- How to estimate ridership for a transit line — a practical, end-to-end guideEstimating ridership is the single most important early exercise in mass transit planning. A realistic ridership estimate tells you whether a scheme is worth designing, what level of service you should provide, and whether further investment in… Read more: How to estimate ridership for a transit line — a practical, end-to-end guide
- What is AADT (Annual Average Daily Traffic) in Traffic Engineering?Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) is one of the most fundamental measures in traffic engineering and transportation planning. It represents the average number of vehicles that travel on a roadway segment each day over the course of… Read more: What is AADT (Annual Average Daily Traffic) in Traffic Engineering?
- Understanding the K-Factor in Traffic EngineeringIn traffic engineering, the K-factor is a critical parameter used in roadway design and traffic analysis. It represents the proportion of Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) that occurs during the design hour, and it allows engineers to… Read more: Understanding the K-Factor in Traffic Engineering
- Climate-Resilient Public Transit: Protecting Buses, Rail, and Depots from Extreme WeatherWhy Public Transit Needs Climate Resilience Public transit systems—buses, metros, trams, and commuter rail—are the lifeblood of urban mobility. As cities grow, they are also frontline services in the fight against climate change. But extreme weather events… Read more: Climate-Resilient Public Transit: Protecting Buses, Rail, and Depots from Extreme Weather
- Innovative Road Design Solutions for Climate ResilienceWhy Roads Must Adapt to a Changing Climate Roads and highways form the backbone of global transport networks. Yet, they are increasingly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change—flooding, extreme heat, erosion, and storm damage. As weather… Read more: Innovative Road Design Solutions for Climate Resilience
- Adapting Road and Rail Networks to Climate Change & Extreme WeatherWhy Climate Resilience Matters Climate change is no longer a distant risk—it is a present-day reality. Rising temperatures, heavier rainfall, stronger storms, and frequent flooding are directly affecting how transport systems operate. Road and rail networks, designed… Read more: Adapting Road and Rail Networks to Climate Change & Extreme Weather
- BRT vs. LRT vs. Metro: Choosing the Right Transit Mode for Your CityUrban mobility is at the heart of sustainable city growth. Around the world, cities face the challenge of moving large numbers of people efficiently, affordably, and with minimal environmental impact. Three of the most common mass transit… Read more: BRT vs. LRT vs. Metro: Choosing the Right Transit Mode for Your City
- ESAL Cheat Sheet: Quick Reference for Pavement EngineersWhat is an ESAL? ESAL Formula Where: Typical Load Equivalency Factors (LEFs) (based on AASHTO & typical LEFs) Vehicle Type Axles Typical Load (kips per axle) Approx. ESAL per Pass Passenger Car (sedan) 2 2–3 0.0004 Pickup… Read more: ESAL Cheat Sheet: Quick Reference for Pavement Engineers
- Understanding Signal Timing Plans: Key Terms and Control TypesTraffic signals are at the heart of modern intersections. Their timing not only dictates how efficiently traffic flows but also affects safety, pedestrian accessibility, and overall network performance. To design or evaluate a signal plan, engineers rely… Read more: Understanding Signal Timing Plans: Key Terms and Control Types
- Revenue Generating Strategies for Public Transit ServicesPublic transit systems are the backbone of urban mobility—moving millions of people daily, reducing congestion, and supporting economic activity. Yet, many agencies around the world struggle with financial sustainability. Farebox revenue alone rarely covers operating costs, and… Read more: Revenue Generating Strategies for Public Transit Services
- How to Build a Transportation (Travel Demand) Model: A Practitioner’s GuideA transportation (travel demand) model is a quantitative framework that forecasts how people and goods move through a region under different land-use and network scenarios. Done well, a model becomes a decision engine: it helps test road… Read more: How to Build a Transportation (Travel Demand) Model: A Practitioner’s Guide
- Sight Distance Requirements in Road DesignSight distance is one of the most important considerations in road design. It represents the length of roadway visible to a driver, ensuring there is enough distance to perceive, react, and stop safely when encountering obstacles or… Read more: Sight Distance Requirements in Road Design
- Good Parking Standards: A Complete Reference for Designers and ArchitectsDesigning a parking lot requires attention to efficiency, safety, and accessibility. Below is a reference guide with parking space dimensions, aisle widths, clearances, layout types, and line-marking standards that designers can use when planning surface or structured… Read more: Good Parking Standards: A Complete Reference for Designers and Architects
- Should You Study Transportation Engineering?Transportation planning and engineering is one of the most dynamic and impactful career paths available today. It sits at the intersection of technology, infrastructure, sustainability, and public policy. If you’ve ever searched “Should I study transportation engineering?”… Read more: Should You Study Transportation Engineering?
- Pass-By Trips: What They Are, How to Calculate Them, and How Not to Get BurnedIf you already work with trip generation, you know the headline challenge in many Traffic Impact Studies (TIS/TIA): not all site trips are “new” to the network. Some are simply siphoned from vehicles already passing by. Getting… Read more: Pass-By Trips: What They Are, How to Calculate Them, and How Not to Get Burned
- What is a Transportation Master Plan?A Transportation Master Plan (TMP) is a comprehensive, long-term strategic document that guides the development, management, and investment in a community’s transportation system. It ensures that transportation networks, roads, public transit, walking, cycling, and freight are planned… Read more: What is a Transportation Master Plan?
- Public Transit Vehicle Types, Capacities, and Use CasesChoosing the right type of public transit vehicle is a balance between passenger demand, operating cost, capacity, and corridor constraints. From standard 12 m buses to high-capacity metro trains, each vehicle type has unique strengths and limitations.… Read more: Public Transit Vehicle Types, Capacities, and Use Cases